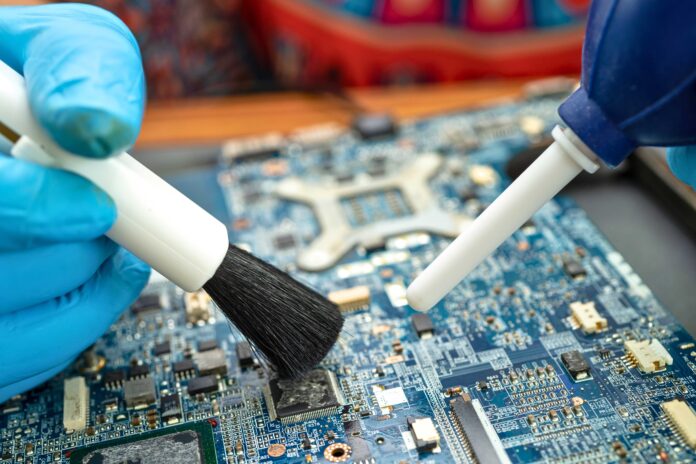
Cleaning circuit boards is a crucial task for maintaining the functionality and longevity of electronic devices. As dirt, dust, and moisture accumulate on a printed circuit board (PCB), it can lead to operational problems, short circuiting, or even complete failure of the device. In this guide, we explore how circuit boards get dirty, methods for cleaning them, tools required for the job, and safety precautions to consider. Let’s delve into the important aspects of cleaning circuit boards.
How Do Circuit Boards Get Dirty?
Circuit boards collect dirt and debris through a variety of means. Everyday use can lead to the accumulation of dust, hair, and other particles, especially when devices are in open environments. Additionally, factors such as humidity and exposure to substances like oils and food residues can lead to grime buildup. Over time, these contaminants can hinder electrical connections, impair performance, and increase the likelihood of corrosion.
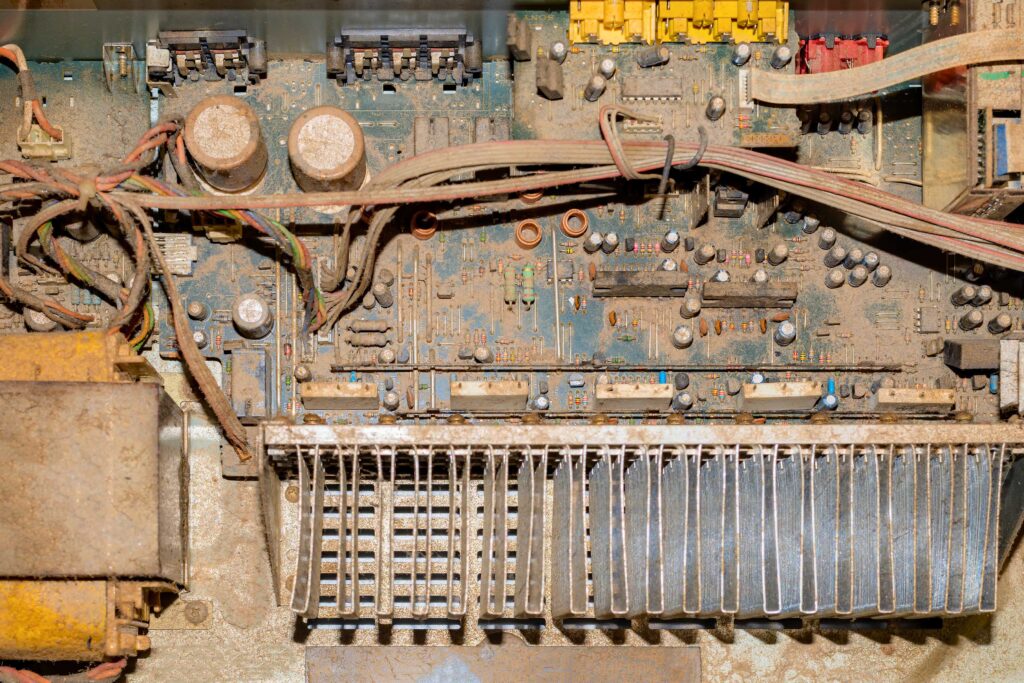
Environmental factors also play a significant role in dirt accumulation. Areas with high amounts of airborne dust, pollutants, or moisture can cause circuit boards to become dirty much faster than those in clean, dry environments. Furthermore, accidental spills from beverages or foods can facilitate further buildup and lead to shorts.
Prevention and Safety with Circuit Boards
Taking proactive measures is always more effective than dealing with the aftermath of damage. To protect your circuit boards from dirt accumulation and potential malfunctions, consider implementing the following strategies:
Cover Devices When Not in Use:
One of the simplest and most effective ways to prevent dust and debris from settling on your circuit boards is to keep devices covered when they are not in operation. Utilize dust covers, bags, or cases specifically designed for electronic devices to shield them from environmental contaminants. This small effort can significantly prolong the life and reliability of your equipment.
Limit Humidity Exposure:
Moisture can wreak havoc on electronic components, leading to corrosion and shorts. It is crucial to store your electronic devices in environments with low humidity. Consider using silica gel packs in storage containers or dehumidifiers in rooms where electronic equipment is kept. By actively controlling humidity levels, you can mitigate the risk of moisture-related damage significantly.
Handle Circuit Boards with Care:
Proper handling of circuit boards is essential in ensuring their longevity. Always ensure your hands are clean and dry, or opt to wear gloves while working with these sensitive components. This precaution helps prevent the transfer of oils, dirt, and moisture from your skin, which can lead to malfunctions over time. Additionally, always be mindful of how you grip and manipulate circuit boards to avoid physical damage.
Utilize ESD Protection:
Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) can pose a severe threat to sensitive electronic components. To prevent any accidental discharge, make sure to employ ESD protection measures such as specialized mats and grounded wrist straps when working on or near circuit boards. By integrating these tools into your workflow, you can safeguard against potentially devastating damage caused by static electricity.
Prioritize Safety When Cleaning:
When it comes to cleaning circuit boards, safety should always come first. It is imperative that devices are completely unplugged before any cleaning begins to avoid electrical shock or damage. Moreover, steer clear of harsh or abrasive chemicals that can harm delicate components; instead, opt for specialized cleaning solutions made for electronics. Ensuring a safe and appropriate cleaning process not only enhances the performance of your circuit boards but also preserves their structural integrity for the long term.
How Do You Clean Circuit Boards?
Using Compressed Air to Clean PCBs
One of the easiest and most effective methods of cleaning a PCB is by using compressed air. This method helps remove dust and debris from the surface without the risk of adding moisture or other substances. To clean a circuit board with compressed air:
Prepare the Area:
Set up your workspace to contain any dust particles.
Hold the Can Upright:
Shake your can of compressed air and hold it upright to prevent any moisture from escaping.
Use Short Bursts:
Apply short bursts of air to dislodge dirt and dust from the circuit board. Keep the nozzle at least a few inches away to avoid damaging any components.
Inspect:
Check if you need to repeat the process in heavily soiled areas.
Using Baking Soda to Clean PCBs
Baking soda is a natural cleaning agent that can help fight oxidation and corrosion on circuit boards. If your PCB has some corrosion or residue, follow these steps:
Make a Paste:
Mix baking soda with water to form a thick paste.
Apply Using a Brush:
Use a soft toothbrush or scrub brush to gently apply the paste on affected areas.
Let it Sit:
Allow it to sit for a few minutes to let it work into the corrosion.
Rinse:
Rinse with distilled water to remove any residue and dry thoroughly before reassembling.
Using Isopropyl Alcohol to Clean PCBs
Isopropyl alcohol (IPA) is one of the most popular solvents for cleaning electronic components, including circuit boards. It’s effective at removing oils, flux, and other contaminants. To clean a circuit board with IPA:
Choose the Right Concentration:
Use at least 70% isopropyl alcohol, but 99% is preferable if available.
Dampen a Cloth
Moisten a lint-free cloth or cotton swab with the alcohol—avoid soaking.
Gently Wipe:
Wipe the circuit board gently, focusing on areas with visible grime or flux.
Dry:
Allow the board to dry completely before plugging it back in.
Using Distilled Water to Clean PCBs
Sometimes, distilled water alone is sufficient for cleaning circuit boards, especially when there’s no heavy contamination. Here’s how:
Rinse:
Use distilled water to rinse off the circuit board.
Scrub if Necessary:
Use a soft brush to dislodge stubborn debris.
Dry Completely:
Ensure the board is completely dry before reassembling, as moisture can cause future issues.
Using Household Cleaners to Clean PCBs
While typically not recommended due to potential residues, some household cleaners can be safely used on PCBs if they don’t contain harsh chemicals. Always check manufacturers’ recommendations before proceeding.
Dilute the Cleaner:
If the cleaner is safe for electronics, dilute it appropriately.
Dampen a Cloth:
Just like with IPA, use a lightly dampened cloth.
Wipe:
Carefully wipe the board, ensuring no liquid runs into the components.
Rinse:
Make sure to rinse it off thoroughly with distilled water and dry effectively.
Essential Tools for Cleaning Printed Circuit Boards
Using the right tools enhances the efficiency of cleaning printed circuit boards (PCBs). A clean PCB ensures optimal performance and longevity, making quality tools a worthwhile investment for hobbyists and professionals alike. Here are some essential cleaning tools:
Compressed Air Can
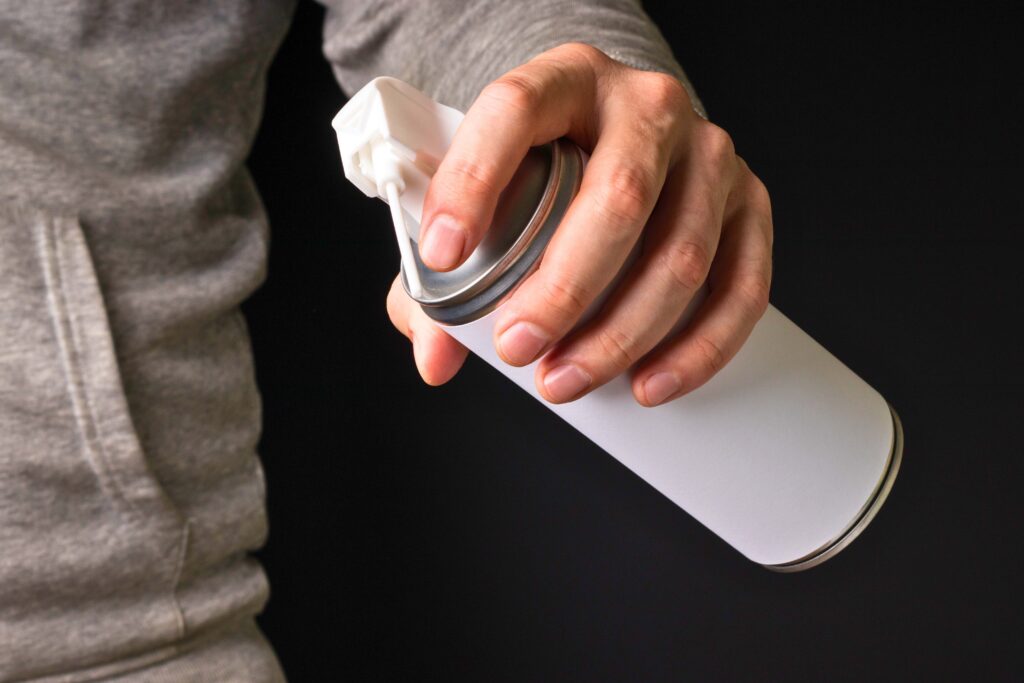

A compressed air canister is vital for swiftly removing dust from PCBs. The air burst dislodges particles in tight spaces, preventing interference with board operation and keeping moisture away from sensitive components.
Isopropyl Alcohol
Isopropyl alcohol is an effective solvent for dissolving grease, dust, and flux residue. With a quick evaporation rate, it minimizes moisture damage to electronic parts. Using at least 90% concentration ensures efficient cleaning and fast drying.
Soft Brushes
Soft brushes are crucial for removing grime without scratching the boards. Nylon bristle brushes work well on stubborn build-up. It’s essential to use them gently to avoid damaging small components or the board surface.
Lint-Free Cloths
Lint-free cloths are necessary for wiping and drying surfaces without leaving fibers that could cause electrical shorts. Using cloths designed for electronics helps effectively remove excess isopropyl alcohol while ensuring a clean surface.
Tweezers
Precision tweezers are important for handling small PCB components safely. They allow careful manipulation without damage. Anti-static tweezers are preferred to prevent static discharge that could harm sensitive electronics.
Distilled Water
Distilled water is often used for rinsing PCBs after cleaning. Its purity prevents mineral residue from tap water, avoiding corrosion. Rinsing with distilled water ensures optimal board condition, and the PCB should dry thoroughly before reassembly or powering on.
What Causes Corrosion in Circuit Boards?
Corrosion on a circuit board arises from various sources, including:
Moisture:
Water or humidity facilitates electrochemical reactions resulting in corrosion.
Salt:
Salt from sweat or the air can significantly speed up the corrosion process.
Fluids:
Spills from beverages or chemicals contribute to corrosion.
Oxidation:
Over time, exposure to air can oxidize metal connections on a PCB.
Corrosion can lead to poor connectivity and, ultimately, device failure, making prevention and maintenance crucial.
How to Clean Corrosion from a Circuit Board
If your circuit board has corroded areas, taking immediate action is vital:
Disconnect Power:
Ensure the device is unplugged.
Identify the Corrosion:
Determine the extent of corrosion and which components are affected.
Use Isopropyl Alcohol:
Gently dab isopropyl alcohol onto the corroded area using a brush or cloth.
Scrub Gently:
Use a soft toothbrush to carefully scrub away corrosion.
Rinse:
Use distilled water to rinse and remove any residue.
Dry Thoroughly:
Before reassembling the device, ensure the area is completely dry.
Steps to Clean a Circuit Board
When cleaning a circuit board, a methodical approach is necessary to avoid damage. Here are the general steps to follow:
Gather Tools:
Collect all necessary cleaning supplies and tools.
Safety First:
Ensure the device is unplugged and you are working in a static-free environment.
Examine Board:
Look for the extent of dirt, dust, corrosion, or any specific contaminants.
Choose Method:
Depending on the condition, decide whether to use compressed air, isopropyl alcohol, or another method.
Clean Each Section:
Work section by section gently to avoid damaging components.
Rinse If Needed: For specific methods that require rinsing, use distilled water.
Dry:
Use a lint-free cloth to dry areas, focusing on moisture trapped in corners.
Inspect Again:
Once dry, examine the board for any missed spots or remaining corrosion.
Reassemble Carefully: When satisfied with the cleaning, reassemble the device with care.
How to Clean a Circuit Board That Got Wet
If a circuit board has gotten wet, immediate action is critical:
Power Down Immediately:
Unplug the device and remove any batteries if applicable.
Dry the Board:
Use a lint-free cloth to blot excess moisture. Avoid rubbing.
Use Isopropyl Alcohol:
Dampen a cloth with isopropyl alcohol and gently wipe the surfaces. This will help displace water and avoid corrosion.
Submersion (If Necessary):
For heavy contamination, you may submerge in a bath of distilled water with isopropyl alcohol for a short period. (Use this method cautiously.)
Dry Again:
Place the PCB in a dry, warm environment (like a window sill, but not in direct sunlight) for at least 24 hours to thoroughly dry.
Inspect:
Check for traces of corrosion or damage before reassembling.
How to Remove Solder Flux From PCB
Removing solder flux is essential for ensuring optimal functionality. Accumulated flux can cause poor connections and operational issues. Here’s how to remove it:
Use Isopropyl Alcohol:
Dampen a soft cloth or cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol.
Gently Rub:
Rub the area with flux gently, using a circular motion to lift the residue.
Rinse if Needed:
For more stubborn flux, lightly scrub it with a brush.
Dry the Area:
After cleaning, ensure the area dries completely.
FAQ
Is it OK to clean a circuit board with alcohol?
Yes, isopropyl alcohol is commonly used and safe for cleaning circuit boards, as it evaporates quickly and does not leave residue.
Can we use WD-40 to clean circuit boards?
WD-40 is not recommended for cleaning circuit boards, as it contains oils that can attract dirt and dust, leading to future problems
What is the best solvent for cleaning circuit boards?
Isopropyl alcohol (preferably 99%) is widely regarded as the best solvent, although distilled water can be used for rinsing.
How do you clean corrosion off a circuit board?
Use isopropyl alcohol or a baking soda paste to scrub away corrosion gently. Rinse with distilled water and dry thoroughly.
What is safe to clean a circuit board with?
Isopropyl alcohol, distilled water, and compressed air are all safe cleaning solutions for circuit boards.
Can you use vinegar to clean circuit boards?
Vinegar is acidic and can damage circuit boards; thus, it is not recommended.
Can you clean a circuit board with tap water?
Tap water contains minerals that can leave residues and is not recommended. Always use distilled water for rinsing.
Can you use hydrogen peroxide to clean a circuit board?
Hydrogen peroxide is generally not recommended for cleaning PCBs, as it can also damage components.
What is the best alternative to rubbing alcohol for cleaning electronics?
If isopropyl alcohol is unavailable, you might consider using distilled water with a gentle surfactant, but be cautious and ensure thorough drying afterward.
Conclusion
Cleaning circuit boards is a vital maintenance process that can significantly extend the life and functionality of electronic devices. By understanding how dust, moisture, and contaminants affect circuit boards, employing the right cleaning methods, and following safe practices, you can effectively clean and maintain your electronic equipment. Always remember that preventive measures, such as covering devices and limiting exposure to moisture, can go a long way in keeping circuit boards clean and operational.
