Field-Programmable Gate Arrays (FPGAs) are integrated circuits designed to be configured by the customer or designer after manufacturing, hence “field-programmable.” This flexibility allows for tailored, high-performance computing solutions that are used in a wide range of applications from consumer electronics to aerospace. This article will explore what FPGAs are, how they work, their applications, and why they might be chosen over other computing solutions like CPUs and microcontrollers. We’ll also touch on their history, design, programming, and major manufacturers. Additionally, we will discuss Arshon Technology’s role in FPGA development and support.
What Is FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array)?
FPGAs are semiconductor devices that consist of a matrix of configurable logic blocks (CLBs) connected via programmable interconnects. Unlike fixed-function devices like Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs), FPGAs can be reprogrammed to perform different tasks, even after they have been deployed. This reprogrammability makes FPGAs extremely versatile and adaptable to changing requirements.
How Does FPGA Work?
FPGAs work by using a combination of programmable logic blocks and interconnects. The logic blocks can be programmed to perform various logical operations, while the interconnects can be configured to route signals between these blocks. This configuration is done using a hardware description language (HDL) such as VHDL or Verilog. Once programmed, the FPGA can operate autonomously, processing data in parallel and offering high-speed performance.
Applications of FPGAs
FPGAs are used in a wide range of applications, including:
Telecommunications
Signal processing and network infrastructure.
Consumer Electronics
Digital signal processing in audio and video equipment.
Automotive
Advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and infotainment systems.
Aerospace and Defense
Radar systems, electronic warfare, and satellite communications.
Data Centers
Accelerating data processing tasks, such as machine learning and encryption.
Industrial Control
Automation systems and robotics.
Why Use FPGA Instead of CPU?
FPGAs offer several advantages over CPUs:
Parallel Processing
FPGAs can process multiple tasks simultaneously, making them faster for certain applications.
Customizability
They can be tailored to specific tasks, optimizing performance and efficiency.
Latency
FPGAs have lower latency compared to CPUs, which is critical in real-time applications.
Energy Efficiency
They can be more power-efficient for specific tasks due to their ability to perform operations in parallel and their customizability.
Is Arduino a FPGA?
No, Arduino is not an FPGA. Arduino is a microcontroller platform that is designed for simple, low-power computing tasks. It uses a microcontroller chip, such as the ATmega328, which has a fixed architecture and is not programmable like an FPGA.
Is the Raspberry Pi FPGA?
No, the Raspberry Pi is not an FPGA. The Raspberry Pi is a single-board computer that uses a general-purpose CPU, typically an ARM processor. While it can be used for a variety of computing tasks and can interface with FPGAs, it does not have the reprogrammable hardware capabilities of an FPGA.
Why Use an FPGA Instead of a Microcontroller?
FPGAs are preferred over microcontrollers in certain scenarios because:
Performance
FPGAs can perform high-speed, parallel processing tasks that microcontrollers cannot match.
Flexibility
They can be reprogrammed to meet new hardware requirements, whereas microcontrollers have a fixed architecture.
Customization
FPGAs can be tailored to perform specific tasks more efficiently than general-purpose microcontrollers.
Scalability
They can handle more complex tasks and larger data sets compared to microcontrollers.
Easy prototyping
Just by relocating the internal connection and configurations inside of the FPGA, we can create new hardware without the need of new PCB and time delay in production.
History of FPGA
The FPGA was first introduced in the 1980s by Xilinx, which remains one of the leading FPGA manufacturers today. The original purpose was to create a programmable logic device that could be configured after manufacturing, offering more flexibility than fixed-function ICs. Over the years, FPGAs have evolved to include more logic gates, memory, and advanced features, making them suitable for a wide range of high-performance applications.
Design of FPGA
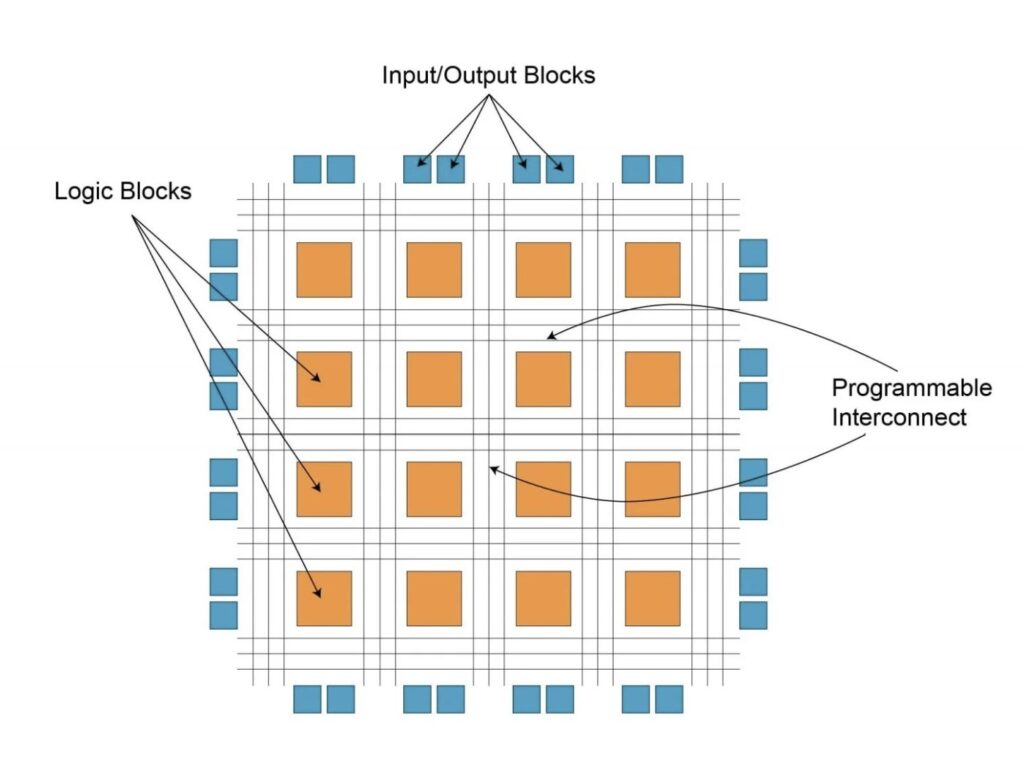
The design of an FPGA involves several key components:
Configurable Logic Blocks (CLBs)
These are the building blocks of an FPGA, capable of implementing a variety of logical functions.
Programmable Interconnects
These connect the CLBs and allow for flexible routing of signals.
I/O Blocks
These interface the FPGA with external devices and signals.
Embedded Memory
Modern FPGAs include on-chip memory for storing data and instructions.
Specialized Blocks
Some FPGAs include dedicated blocks for tasks like digital signal processing (DSP), high-speed I/O, and memory controllers.
FPGA Programming
Programming an FPGA involves using a hardware description language (HDL) such as VHDL or Verilog to describe the desired logic and behavior. This HDL code is then synthesized into a configuration file that can be loaded onto the FPGA. The process typically involves several steps:
Design Entry
Writing the HDL code to describe the logic.
Synthesis
Converting the HDL code into a netlist of logic gates.
Implementation
Placing and routing the logic gates on the FPGA.
Verification
Simulating the design to ensure it behaves as expected.
Programming
Loading the configuration file onto the FPGA.
FPGA Manufacturers
Several companies manufacture FPGAs, including:
Xilinx
One of the pioneers in the FPGA market, known for their high-performance and versatile FPGAs.
Intel (formerly Altera)
Intel offers a wide range of FPGAs for various applications, including data centers and automotive.
Lattice Semiconductor
Known for low-power and small-form-factor FPGAs.
Microsemi
Provides FPGAs with a focus on security and reliability for aerospace and defense applications.
Arshon Technology: Leading the Way in FPGA Solutions
Arshon Technology is a leader in providing FPGA-based solutions and services. With a team of highly skilled engineers and state-of-the-art tools, Arshon Technology offers comprehensive FPGA design, development, and support. Their services include:
Custom FPGA Design
Tailoring FPGA solutions to meet specific application requirements.
FPGA Prototyping
Rapid prototyping and development to accelerate time-to-market.
FPGA Verification and Testing
Ensuring the reliability and performance of FPGA designs.
Training and Consultation
Providing expert guidance and training on FPGA design and implementation.
Arshon Technology’s commitment to innovation and excellence ensures that their clients receive the best possible FPGA solutions, whether for high-speed data processing, telecommunications, automotive, or other advanced applications.
Conclusion
FPGAs offer unparalleled flexibility and performance for a wide range of applications, from telecommunications to consumer electronics and aerospace. Understanding their unique capabilities and design considerations is crucial for leveraging their full potential. With the expertise and support of companies like Arshon Technology, engineers can navigate the complexities of FPGA design and implementation to achieve optimal results.
Whether you’re considering an FPGA for its parallel processing capabilities, reprogrammability, or customization options, it’s clear that these devices play a vital role in modern electronic design. As technology continues to advance, the importance of FPGAs and their applications will only grow, making them an essential component in the toolkit of any electronics engineer.
