In the world of electronics manufacturing, terms can often be confusing, especially for those who are new to the field or are considering venturing into it. One such pair of terms that frequently perplexes people is PCB and PCBA. While they may seem similar at a glance, they represent distinctly different concepts that are key to understanding how electronic devices are made. In this blog post, we will delve into what PCBs and PCBAs are, their differences, and their importance in the various stages of electronics manufacturing.
Understanding PCB (Printed Circuit Board)
What is a PCB?
A Printed Circuit Board (PCB) is a fundamental component used in electronic devices to provide mechanical support and electrical connections among electronic components. A PCB consists of a flat board made from non-conductive materials such as fiberglass, plastic, or composite epoxy, to which conductive pathways are etched or printed. These pathways allow electrical signals to travel between various components, creating circuits that facilitate the functioning of different electronic devices.
Components of a PCB
Substrate: The base material of the PCB, typically made of fiberglass, provides structural support and insulation.
Copper Layer: Conductive pathways are created from copper sheets either deposited or etched onto the substrate, forming traces that connect different points on the PCB.
Solder Mask: A protective layer that covers the copper traces to prevent oxidation and to prevent solder from bridging between conductors.
Silkscreen: Usually printed on the surface of the board, this layer contains information such as component designators, logos, and other identifiers.
Via: A small hole in the PCB that allows electrical connections between different layers.
Types of PCBs
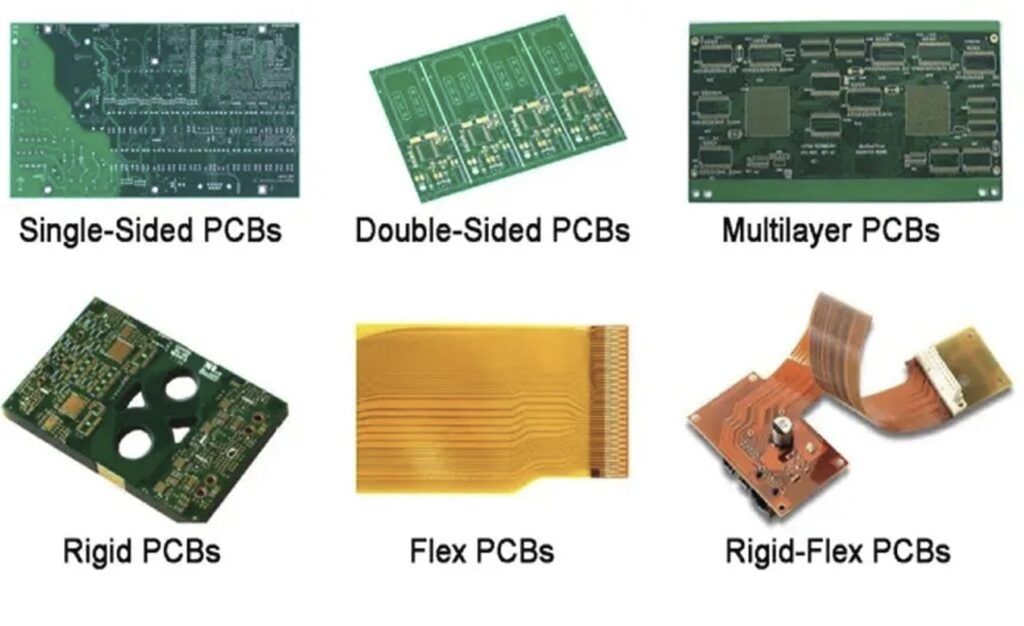
PCBs come in various types based on their structure and functionality:
Single-Sided PCBs: Have a single layer of conductive material on one side only.
Double-Sided PCBs: Feature conductive layers on both sides, allowing for a denser arrangement of circuits.
Multilayer PCBs: Comprise several layers of circuits sandwiched together, enabling complex applications.
Rigid PCBs: Made from inflexible substrates, they maintain their shape and structure when assembled.
Flexible PCBs: Designed to bend and flex, these are made with flexible materials, suitable for compact spaces.
Rigid-Flex PCBs: A combination of rigid and flexible technologies, providing the benefits of both.
Understanding PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly)
What is a PCBA?
A Printed Circuit Board Assembly (PCBA) refers to a fully assembled PCB that includes not just the board itself but also the various electronic components that have been soldered onto it. In essence, while a PCB is just the base board, a PCBA is the complete, functional assembly that can operate as part of a larger electronic system.
Components of a PCBA
PCB: The underlying base that forms the structure of the assembly.
Electronic Components: These include resistors, capacitors, diodes, microcontrollers, integrated circuits, and other components soldered onto the PCB.
Interconnections: Wires or traces that connect the components, allowing for current and signal flow.
Solder: The metal alloy used to bond the component leads to the PCB.
Processes Involved in PCBA
The process of creating a PCBA involves several key steps:
Design: Engineers design the layout of the PCB using software tools, specifying where each component will be placed.
Fabrication: The PCB is manufactured according to the design specifications.
Components Placement: Electronic components are placed on the assembled PCB, typically using automated machines for efficiency.
Soldering: The components must be soldered onto the board, which can be done through methods such as wave soldering, reflow soldering, or hand soldering.
Inspection and Testing: After assembly, the PCBA undergoes thorough inspection and testing to ensure its functionality and reliability.
Encapsulation/Coating: Depending on the application, a protective coating may be applied to the PCBA to shield it from environmental factors.
Key Differences Between PCB and PCBA
Definition:
PCB: Refers to the bare board that has conductive pathways but does not have any electronic components attached.
PCBA: Represents a complete assembly where electronic components are soldered onto the PCB.
Functionality
PCB: Serves primarily as the structural base for the electrical circuits.
PCBA: Functions as an integral part of an electronic device, enabling it to perform its designated tasks.
State of Assembly
PCB: Is an unassembled board; it does not contain any components, making it non-operational.
PCBA: Is an assembled board that is fully operational, including all necessary components soldered onto it.
Complexity
PCB: Generally simpler in design since it consists only of the board itself with traces.
PCBA: More complex due to the inclusion of multiple electronic components such as resistors, capacitors, and microcontrollers.
Cost
PCB: Typically incurs a lower cost, as it only consists of the bare board without components.
PCBA: Has a higher cost due to the additional components and the labor required for assembly.
Manufacturing Process
PCB: Involves the design and fabrication of the board itself.
PCBA: Encompasses the entire process, including PCB manufacturing, component placement, and soldering to create the final assembled product.
Additional Considerations
Design Flexibility: When designing a PCB, there is tremendous flexibility to optimize the layout for size, cost, and functionality. In contrast, the design of a PCBA must take into account the placement of components, ensuring they fit together correctly without interfering with one another.
Testing Procedures: Testing a PCB is an essential part of the manufacturing process, as any defects in the board itself can lead to component failures later. On the other hand, PCBAs undergo more comprehensive testing that evaluates both the board and the components together to ensure that the final product performs as intended.
Production Volume: The type of production — whether it is for single units or high volumes — affects the cost and complexity of both PCBs and PCBAs. Generally, PCBs are produced in larger quantities due to the demand for them in PCBA manufacturing.
Importance of PCB and PCBA in Electronics Manufacturing
Both PCBs and PCBAs play crucial roles in the electronics manufacturing industry:
Cost-Effectiveness
PCBs form the backbone of electronic devices, providing a cost-effective way to interconnect electronic components in a compact manner. By carefully designing the PCB, manufacturers can reduce material costs and complexity.
Performance Reliability
The quality of the PCB directly affects the reliability of the entire assembly. Poor-quality PCB designs can lead to failures, which makes it essential to focus on high-quality PCB fabrication processes.
Design Optimizations
The development of PCBs and PCBA technologies has enabled engineers to create smaller, more powerful devices while still ensuring ease of manufacturing. Continuous advancements in design software and manufacturing techniques allow for innovative solutions in product design.
Rapid Prototyping
With the rise of rapid prototyping technologies, companies can design, manufacture, and assemble PCBs quickly, allowing for faster iterations and reduced time-to-market for new products.
Customization
PCBAs can be tailored to meet specific requirements for a given application, providing the flexibility needed in a diverse range of industries, from consumer electronics to automotive to medical devices.
As a leader in the electronics manufacturing sector, Arshon Technology specializes in PCB design and manufacturing, alongside PCB assembly services. With a commitment to innovation and efficiency, the company utilizes advanced techniques and state-of-the-art equipment to deliver products that consistently exceed industry standards. Maintaining a strong focus on quality control and customization, Arshon Technology collaborates with clients across various sectors to provide tailored solutions that address specific project needs. This ensures that every electronic device is both reliable and cutting-edge. Their expertise empowers engineers and manufacturers to transform innovative concepts into tangible products, driving advancements in technology and the electronics industry as a whole.
Conclusion
In summary, while PCB (Printed Circuit Board) and PCBA (Printed Circuit Board Assembly) may sound similar, they refer to distinct stages in the electronics manufacturing process. The PCB serves as the foundation that facilitates electrical connections among components, while the PCBA represents the fully assembled product, ready for integration into electronic devices. Understanding the differences between these terms is vital for anyone involved in electronics design or manufacturing, as it helps clarify the processes and considerations involved from the initial design phase all the way to a functional product.
As electronic devices continue to evolve and become more complex, so too will the importance of PCBs and PCBAs in driving innovation and efficiency in the industry. Whether you are a seasoned engineer or just beginning your journey in electronics, grasping these concepts is essential for navigating the fascinating world of technology creation.
